access the application with desktop clients [since
1.5]
In the previous pages we have seen how develop
a web application with OBEROn; in particular how create web-forms
to edit / show the property values of object instances and how these
forms are displayed dynamically with Java Server Pages.
Access through web-browsers is only one of the possible ways for connecting to the OBEROn database and performing actions with object instances: another modality is through portable desktop clients based on the Eclipse SWT library.
There are two main classes included inside the OBEROn Platform package that allows you
to develop a desktop client:
-  Application: is the basic class for desktop (SWT) applications. It includes connection methods and other utility functions. This is also the primary class for the administration tools: the "Enterprise Context Design" and "Domain Object Manipulation" consoles. Application: is the basic class for desktop (SWT) applications. It includes connection methods and other utility functions. This is also the primary class for the administration tools: the "Enterprise Context Design" and "Domain Object Manipulation" consoles.
-  OberonClient:
is a primal SWT desktop client; custom SWT clients should extend this class. OberonClient:
is a primal SWT desktop client; custom SWT clients should extend this class.
Desktop clients can be used inside the local intranet;
in some cases they result faster than browser clients because the
computational load is distributed to the client machines instead
of to be concentrated in the application server. To reduce the network
traffic the better configuration is to connect the clients through
RMI or HTTP interfaces to
an RMI / HTTP server.
The OberonClient class contains all basic functionalities
for developing a simple SWT application; you can open it by running
the "startclient.bat" (.sh) script from the SO command line. The
client reads some configuration
parameters from the oberon.ini file; in particular if
you set the configuration parameters "uid" and
the "pwd" you can avoid (if they are correct) to
authenticate yourself every time you open the client. Moreover,
you can set the "application" parameter to avoid
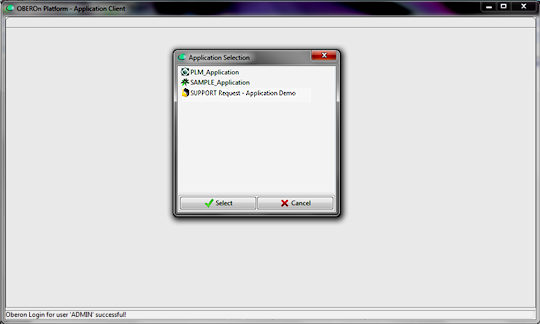
to select the application on startup. Infact, the OberonClient is
a generic client and it can act as the application you want to be.
To define the possible actions that each user can execute
inside the application you must create a set of commands organized
into menus and submenus. Menus created for a web-application can
be used also in desktop clients. The root of a menu/command structure
represents the main-menu and so the application itself. You can
set the "application" parameter with the name of the application
(or portfolio) main menu or you can omit this parameter and select from the list
of application menu roots. When an application menu is selected,
the client loads its sub-structure, including the features representing
the application
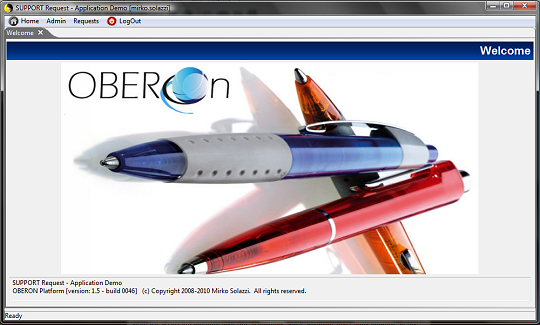
parameters. The first "page" the client shows is the
welcome page.
The mechanism that is used inside the client to pass from a page
to another is similar to the http request/response. The classes
"ApplicationRequest"
and "ApplicationSession"
have the same behaviour of the well-known HttpServletRequest and HttpSession
used in a web context.
The most important method of a desktop client class
(OberonClient or its derivation) is:
handleRequest(ApplicationRequest
request)
This method redirects the input request to another specific
method according to the requested page (or URL) declared inside
the ApplicationRequest itself. It means that for each web URL associated
with menu commands there should be a method that represents the
equivalent web-page in SWT format, like in the following example:

The "TAGS.PAGE_<PageName>" constant values correspond to the web page names (for example "edit.jsp" / "files.jsp" / "lifecycle.jsp" ..... )
Note: page URLs inside the command Href parameter may start with
the webapp relative path; for this reason you should use the "endsWith"
or "indexOf" comparison operators instead of "equals".
The window manager in a desktop client is implemented by two methods:
createPagePanel : prepares the page layout adding the title bar with title / subtitle, object contextual menu (when required) and manages error messages.
addPageToContainer: add the page panel to the proper page container accordind to the ApplicationRequest target; if target is:
-
"" (empty) uses the same container of input request referer
- "_blank"
opens a new tab folder
- "<Window Name>"
replace the content of popup dialog with corresponding name
The first page opened after the login is the TAGS.PAGE_Home (equals to "home.jsp")
renderized by the doHome method.
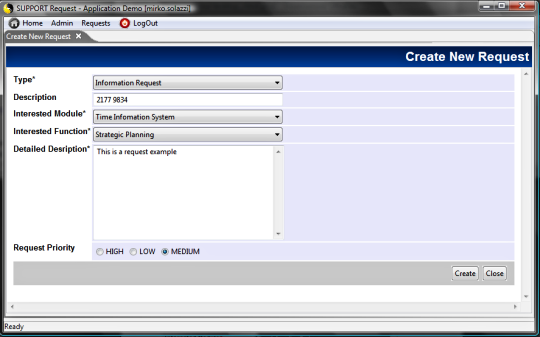
The following examples show how basic functionalities are implemented with SWT controls.
TAGS.PAGE_Edit = edit.jsp -> doEdit
The following method can perform both the object
creation and the object data update (if the input ID is passed as
input parameter). It also manages both the user interface for data
input (createForm) and the database update process (saveFormData).
These two methods are defined into the Forms
class. The Forms class represents the SWT implementation for
the form administrative objects: in other words it generates the SWT
java code based on the form parameters and on the form-item parameters,
included all the code needed to load/refresh the field ranges and
to validate the field-item values.
public void doEdit(ApplicationRequest
request) {
try
{ |
| |
ApplicationSession session = (ApplicationSession) request.getSession();
// Get the object
id as input parameter
String sID = request.getParameter(TAGS.id);
ObjectObj object;
boolean bCreateNew;
boolean bClone = false;
if ( sID==null
|| sID.length()==0
|
| |
|
|| HTMLUtil.getInputParameter(TAGS.create,request).equals("true")
) {
// Create a new
object
bCreateNew=true;
object = new ObjectObj(); |
| |
} else
{ |
| |
|
// Open the object
and read its properties
sID=sID.trim();
bCreateNew=false;
if (HTMLUtil.getInputParameter(TAGS.clone,request).equals("true")
) {
bClone = true;
}
object = ObjectObj.open(sID,true,framework); |
| |
}
// Get the create/edit Form name
as input parameter
String sFormName = HTMLUtil.getInputParameter(TAGS.form
, framework);
if ( sFormName.length()==0)
{ |
| |
|
// When the form
is not passed as input parameter try to get it from the
object class
sFormName = object.getClass(framework).getDefaultForm(true); |
| |
}
Form form = Form.open(sFormName , framework , null );
// Save the object data or create
it
String sForwardPage=Forms.saveFormData(bCreateNew?TAGS.PAGE_Edit:"",object,form,request);
if ( sForwardPage.length()>0
) { |
| |
|
//
A new object is succesfully created - go forward to the
object detail page
ApplicationRequest fwrequest = new ApplicationRequest
(sForwardPage,request.getForwardTarget(),session);
fwrequest.setLocale(request.getLocale());
fwrequest.setReferer(request.getReferer());
handleRequest(fwrequest);
return; |
| |
}
// Define
title and subtitle for the menu bar
String sTitle = Dictionary.getKey(dictionary_Section,sFormName,framework);
String sSubTitle = "";
if ( sID!=null
&& sID.length()>0
) { |
| |
|
if
(bCreateNew) {
//
Clone an existing object
object
= ObjectObj.open(sID,true,framework);
object.resetID();
}
sSubTitle=sTitle;
sTitle= getClassNameRevision(object,session); |
| |
}
// Creates
the page container (includes the menu bar with title and
subtitle)
Composite globalpanel = createPagePanel(sTitle,
sSubTitle, !bCreateNew, request);
if (globalpanel!=null)
{ |
| |
|
// Generate the
SWT form compiled with object field values
ScrolledComposite panel=Forms.createForm(globalpanel,TAGS.PAGE_Edit,object,form,request);
panel.setLayoutData(new
GridData(GridData.FILL_BOTH));
// Add the page container to
the application shell (tab item or dialog shell)
String sPrefix = sSubTitle.length()>0?"("+sSubTitle.substring(0,1)+")
":"";
addPageToContainer(globalpanel,sPrefix+sTitle,request); |
| |
} |
}
catch (Exception
ex) { log(ex.getMessage()); }
} |
|
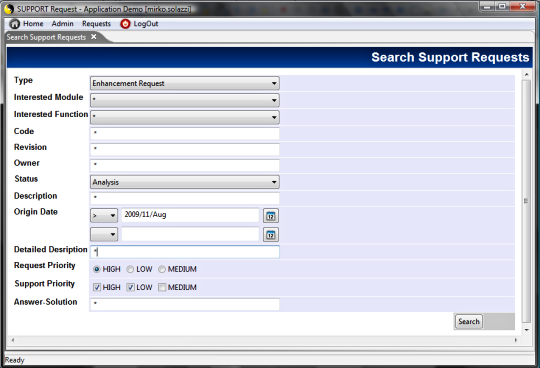
TAGS.PAGE_Search = search.jsp
-> doSearch
The doSearch method is similar to the doEdit: it
manages the user interface for the query input filters (createSearchForm);
this method is also defined into the Forms class. It requires
the search form name as input value and generates the SWT code based
on this form parameters and on its item parameters.
public
void doSearch(ApplicationRequest request)
{
try
{ |
| |
ApplicationSession session = (ApplicationSession) request.getSession();
// Get the search Form name as
input parameter
String sFormName = HTMLUtil.getInputParameter(TAGS.form , request);
if ( sFormName.length()==0)
{ |
| |
|
log("NO
INPUT FORM");
return; |
| |
}
Form form = Form.open(sFormName , framework , null );
String sTitle = Dictionary.getKey(dictionary_Section,sFormName,framework);
|
| |
// Creates
the page container (includes the menu bar with title and
subtitle)
Composite globalpanel = createPagePanel(sTitle,
"",false,
request);
if (globalpanel!=null)
{ |
| |
|
//
Generate the SWT form compiled with object field values
ScrolledComposite panel = Forms.createSearchForm(globalpanel,TAGS.PAGE_SearchResults,form,request);
panel.setLayoutData(new
GridData(GridData.FILL_BOTH));
// Add the page container to
the application shell (tab item or dialog shell)
addPageToContainer(globalpanel,sTitle,request); |
| |
} |
}
catch (Exception
ex) { log(ex.getMessage()); }
} |
|
TAGS.PAGE_SearchResults = search_results.jsp
-> doSearchResult
This method executes the search query based on the
filters defined into the doSearch. It employs the searchObjects method
included into the Forms class. In addition, you can apply a
view to the query results to extract and show several object properties.
public
void doSearchResult(ApplicationRequest request)
{
try
{ |
| |
ApplicationSession session = (ApplicationSession) request.getSession();
// Get the search Form name as
input parameter
String sFormName = HTMLUtil.getInputParameter(TAGS.form , request);
if ( sFormName.length()==0)
{ |
| |
|
log("NO INPUT
FORM");
return; |
| |
}
Form form = Form.open(sFormName , framework , null );
String formHTMLName=Forms.getFormHTMLName(form);
// Execute the search query
try { |
| |
|
String sMessage = Forms.searchObjects(
form , request );
if (sMessage.length()>0)
{
if
(sMessage.startsWith(TAGS.FORM_ActionAlert+"("
)) {
sMessage=
StringUtils.getStringPart( sMessage,TAGS.FORM_ActionAlert+"(\"", "\");"
);
}
Application.showMessage(shell,sMessage,"",SWT.ICON_WARNING);
} |
| |
} catch
(Exception e) { |
| |
|
log(e.getMessage()); |
| |
}
// Get user views
Vector vViews = View.getUserViews(framework);
// Prepare the view list
String sViews = HTMLUtil.getInputParameter(TAGS.views ,request);
Vector vFormViews = StringUtils.StringTokensToVector(sViews,"|");
for (int i=vViews.size()-1;i>=0;i--)
{ |
| |
|
if
(vFormViews.indexOf(((String)vViews.elementAt(i)))<0)
{ vViews.removeElementAt(i);}
|
| |
}
String sView = HTMLUtil.getInputParameter(TAGS.view,request); |
| |
// Creates
the page container (includes the menu bar with title and
subtitle)
Composite globalpanel = createPagePanel(sTitle,
"",false,
request);
if (globalpanel!=null)
{ |
| |
|
//
Generate the SWT table for search result
ResultSetPanel rst = new ResultSetPanel(globalpanel,request);
// Load the view list in the
result set panel
rst.resetViews(sView,vViews);
// Process the search result
Vector
rst.process( Forms.getSearchResults( formHTMLName
, session ) );
// Add mouse listener to the
table items
Table table = rst.getTable();
setData(table,TAGS.request,request);
table.addListener(SWT.MouseUp, ............. );
// Add the page container to
the application shell (tab item or dialog shell)
addPageToContainer(globalpanel,sTitle,request); |
| |
} |
}
catch (Exception
ex) { log(ex.getMessage()); }
} |
|
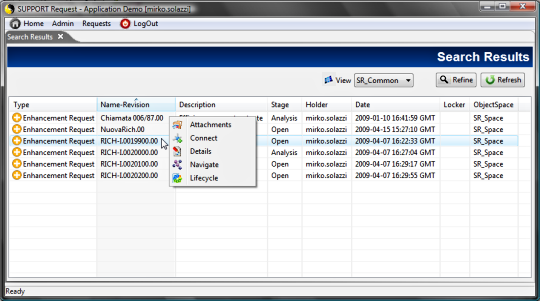
TAGS.PAGE_Files = files.jsp - doFiles
This method shows the object's attached files and
enables the user to perform operations on them (open, extract into
a local folder, attach more , remove )
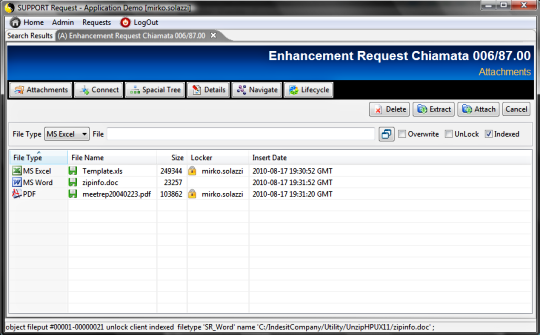
TAGS.PAGE_Lifecycle = lifecycle.jsp -> doLifecycle
This method loads the object's lifecycle and
generates its graphical representation. The user will be able to
progress or regress the status and to validate/refuse the path validations.
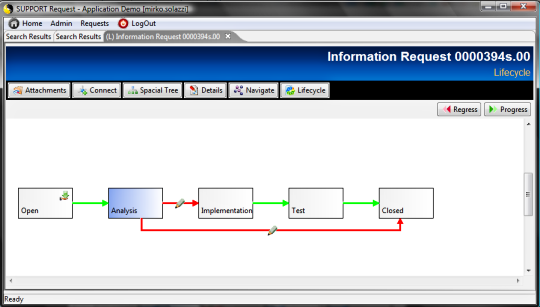
TAGS.PAGE_Navigate = navigate.jsp -> doNavigate
Shows the object's navigation tree: links can
be filtered selecting the linktype and the direction.
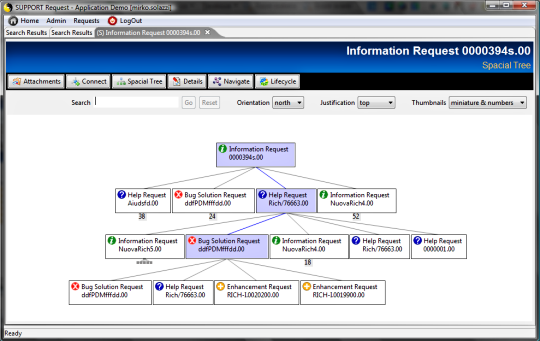
TAGS.PAGE_SpaceTree = spacetree.jsp -> doSpaceTree
Visualizes the object's links by a spacial tree
representation.
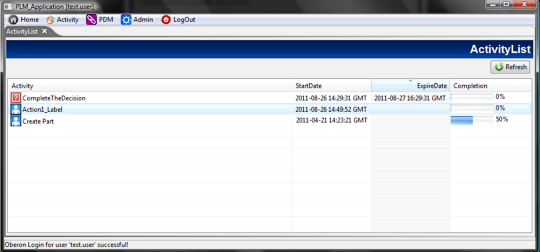
TAGS.PAGE_Activity = activity.jsp -> doActivityList
TAGS.PAGE_ActivityCompletion=default_step_completion.jsp ->doActivityCompletion
Visualizes the user activity dashboard and open
the default completion popups when Href is not specified in workflow
steps.
NOTE: for old versions before the 4.0, it's very important to note that if the application server
connects to the database indirectly through a HTTP / RMI
interface all java API methods with the "framework"
input argument don't work properly. In this case (iit is a best practice
to do it always) you MUST use the JRClient class methods to perform the operations.
|
















